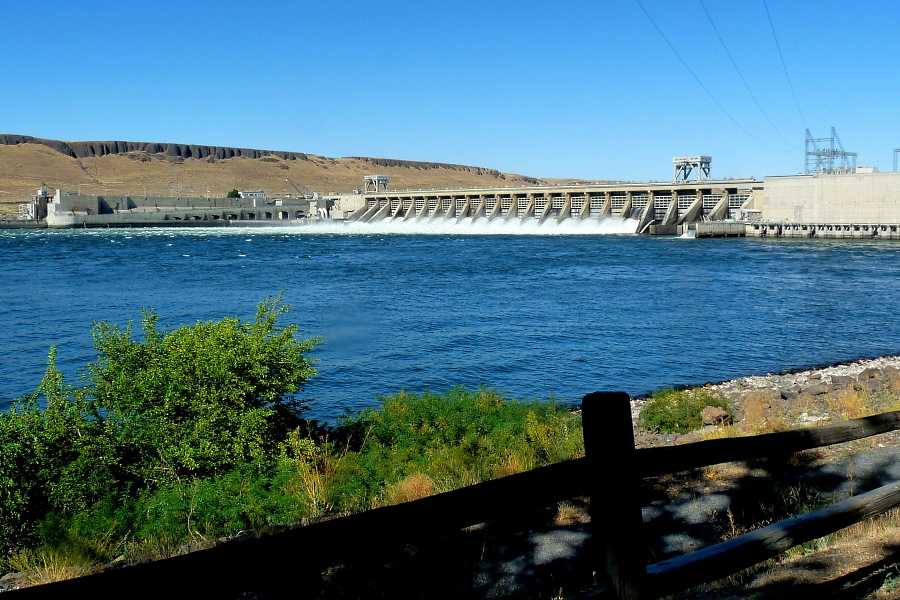
Financing and construction of hydroelectric power plants (HPP)
GCAM Investment Group offers:
• Investment financing from €50 million and more
• Minimizing the contribution of the project promoter
• Investment loan term up to 20 years
• Loan guarantees
According to the Energy Information Administration of the US Department of Energy, hydropower continues to be one of the largest renewable energy sources in the world.
Due to global warming, depletion of fossil fuels and volatile oil prices, countries around the world are focusing on developing renewable energy strategies as part of the global green energy transition.
The hydropower sector plays a critical role in this transition, ensuring the stability of the energy system.
Currently, the largest countries in the world produce the bulk of renewable energy using water. In particular, China is the leader in the hydropower production (1,145 TWh), which is significantly higher than the indicators of Canada and Brazil, which rank second and third in the ranking with values of 388 TWh and 367 TWh, respectively.
GCAM develops comprehensive solutions for the financing and construction of power plants of any size under an EPC contract.
Thanks to our partners, advanced hydropower technology and knowledge, we are ready to offer customers a full range of hydropower equipment from leading manufacturers with turnkey installation and setup.
We actively cooperate with world famous companies around the world, offering customers innovative solutions on favorable terms. Engineering services are always business-specific and combine quality, efficiency and durability.
The services of engineering team include the following:
• Feasibility study.
• Obtaining official permits and licenses.
• Development of technical documentation for the hydroelectric power plant.
• Design, procurement and supply of electrical equipment and hydro turbines.
• Full cycle of construction works, including the construction of reservoirs.
• Construction of substations and connection to the power grid.
• Testing and commissioning of the facility.
• Operation and maintenance.
• Modernization of HPPs, etc.
The developed hydroelectric power plants provide reliable power supply to industrial enterprises, settlements and entire regions, increasing the stability of the power grid.
Engineering solutions of our partners are highly efficient and reliable throughout the entire life cycle of the project.
Experience based on the successful implementation of energy projects in many countries of the world will be the key to the success of your business.
Contact GCAM to learn more about engineering team.
We will find the optimal solution for any energy facility.
Construction of hydroelectric power plants: clear benefits
Historically, hydropower was one of the earliest renewable energy sources.As a technologically simple and reliable technology, HPPs of various types have been actively developed around the world for more than a century.
This led to a situation in which most of the natural reservoirs in Europe and other regions of the world were already used at the beginning of the 21st century.
Currently, the leaders in the pace of construction of hydroelectric power plants are the countries of East Asia, which need cheap electricity for their growing industries. Growth in hydropower in Europe and North America has slowed significantly, reaching a peak in the last years of the last century.
However, in most countries there are still ample opportunities for the development of this sector, including by expanding the network of so-called small hydropower plants. This opportunity is not fully exploited, and hydropower itself has become a subject of environmental and political discussions in a number of EU countries and beyond.
Along with other renewable energy sources, hydropower provides a progressive phase-out of fossil fuels. In recent decades, hydroelectric power plants have gained particular importance due to their ability to smooth out generation fluctuations caused by solar and wind power plants.
Understanding the benefits of hydropower is important for investors.
This helps to carefully weigh the strengths and weaknesses of various energy sources, finding the best options for the implementation of specific business projects.
Table: Key benefits of building hydroelectric power plants.
| Advantage | Brief explanation |
| Flexibility | HPPs can quickly adapt to changing market needs by increasing or decreasing energy production. The hydroelectric power plant can be started up within a few minutes. |
| Minimum CO2 emissions | Hydroelectric power plants mean no carbon dioxide. Minor CO2 emissions can only occur during construction. According to the Paul Scherrer Institute (Switzerland), hydropower ranks first in the ranking of energy sources with the lowest CO2 emissions. It is followed by wind, nuclear and solar energy. |
| Low energy cost | The main advantage of the HPPs is the absence of fuel costs, because renewable energy sources are used to generate electricity. Also, hydroelectric power plants have a long service life (some can work up to 100 years). As a result, the final cost of electricity is significantly lower than that of other types of power plants. |
| Reservoirs ensure the safety of humanity | Despite their controversial ecological role, the reservoirs protect the surrounding area from flooding by trapping excess water. The reservoirs also serve as sources of water for irrigation and drinking, as a place for summer holidays or for practicing various water sports. |
| Obvious economic benefit | In developed countries, a significant part of energy production may be the capacity of thermal and nuclear power plants, which are not able to quickly reduce electricity generation during periods of nighttime energy consumption reductions, or they do it with significant losses. In such conditions, the use of pumped storage power plants significantly increases the efficiency of using other sources. |
| Stable electricity production | Modern hydroelectric power plants, unlike solar power plants and wind farms, are practically unaffected by weather conditions and continue to generate energy at any time of the day or night. |
When choosing an energy source for a specific project, our engineering team conducts numerous studies.
We focus on customer needs and current standards, developing optimal business solutions.

The main types of hydroelectric power plants
Hydroelectric power plants are energy facilities that convert the kinetic energy of a water flow into electrical energy.Modern HPPs are classified according to their size and principle of operation.
Small hydroelectric power plants
Small hydropower facilities are considered the most flexible and affordable solutions with an installed capacity from several kilowatts to several megawatts for supplying power to remote industrial enterprises, small settlements and farms, hotel complexes and other remote facilities.Each country applies its own SHPP criteria, depending on the installed capacity.
Large hydroelectric power plants
Large hydropower plants are widespread in the world and are considered the cheapest sources of renewable energy.These facilities are capable of supplying affordable electricity to large cities and industrial centers.
Despite such advantages as saving fossil fuels, this type of power plant has many disadvantages. Large hydroelectric power plants usually require the construction of huge reservoirs that destroy local ecosystems and have detrimental effects on the environment. It should also be borne in mind that the initial investment costs for their construction are very high.
Depending on the method of using water resources, experts distinguish the so-called flow-through HPPs, dam HPPs, derivation HPPs, as well as pumped storage hydroelectric power plants, which are used to store energy.
Flow-through hydroelectric power plants
Flow-through HPPs use the energy of water flow and are installed only in sections of the river with a sufficiently strong current.These facilities do not require the construction of reservoirs, due to which investment costs are significantly reduced, and negative social and environmental consequences are minimal.
On the other hand, flow-through hydroelectric power plants are completely dependent on the speed of water flow at any given time. There are relatively few suitable sites for the construction of such facilities, and the capacity of hydro turbines is significantly limited.
Dam hydroelectric power plants
A feature of the dam hydroelectric power plants are reservoirs that can hold millions of cubic meters of water.The reservoir compensates for seasonal fluctuations in the amount of flowing water, thanks to which the power plant is able to produce more electricity than under the influence of a normal flow.
Derivation hydroelectric power plants
Derivation HPPs are equipped with special water conduits, which ensure sufficient water pressure due to the required bottom slope.This design allows the environmental conditions to be corrected for efficient power generation. Facilities of this type are built on those sections of rivers where the natural slope of the river is insufficient or excessive (for example, mountain rivers).
Pumped storage hydroelectric power plants
Pumped storage power plants are facilities designed to store energy and provide more stable daily electricity generation.They have two large reservoirs that allow energy storage during periods of low demand by pumping water from the lower reservoir to the upper one. During periods of increased demand for electricity, it is emptied by draining from the upper reservoir to the lower one, which drives the turbine.
These power plants are very expensive, but today it is difficult to find another option for storing such large amounts of energy resources. In the event of a power system failure, this power plant starts the operation of the turbines, compensating for the increased demand for electrical energy. The reservoir is then refilled with water.
In most cases, pumped storage power plants are built near large consumers.
This makes them a key link in the modern energy system, which allows you to store excess energy and use it as needed.
Tidal hydroelectric power plants
Tidal hydropower plants use the ebb and flow of the sea or ocean.The estuaries of the rivers are separated by dams in such a way that the water through the turbine enters the reservoir at high tide and is discharged back into the sea at low tide.
Unfortunately, there are very few places in the world where large tidal hydroelectric power plants can be built. The power generated by these hydroelectric plants can be obtained in about 20 regions, including China, Russia, France and the UK.
Ocean thermal hydroelectric power plants
Electricity can be generated as a result of the temperature difference between the warm surface layers and the cold layers that come from the deep sea.Experimental power plants operating on this principle use freon, ammonia or propane as a working fluid, which evaporate at a temperature of 30 ° C of water and condense with water at a temperature of about 70 ° C. Energy facilities of this type can be found, for example, in Japan or Hawaii.
In recent decades, other types of hydroelectric power plants have also been developed, including facilities that use the energy of sea currents.
For each case, it is important to choose the right electricity generation technology that will best suit the client's needs and the project budget.
Supply of equipment for hydroelectric power plants
The choice of equipment for the construction of hydropower plants is a complex technical task that requires a series of studies and comparative analyzes, as well as multi-stage consultations with the client and potential suppliers.Our multidisciplinary team will take care of all your concerns.
The HPP equipment list includes various types of turbines, generators, electric motors, water pumps, pipelines, shut-off equipment and much more. We suggest taking a closer look at the equipment listed above in order to get a better idea of the work ahead.
If you need detailed information, please contact our consultants at any time.
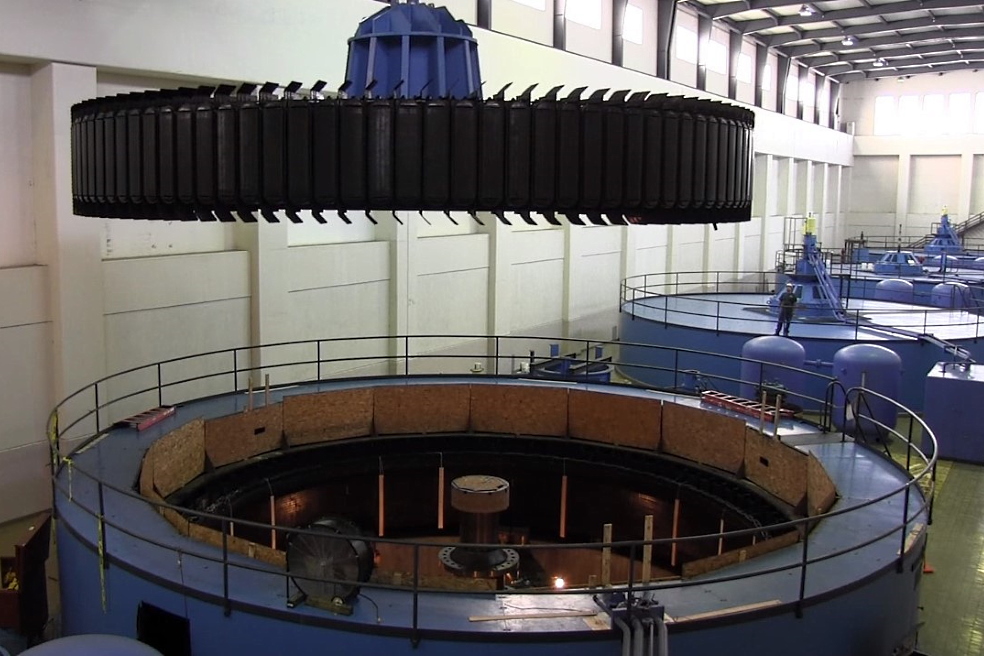
Hydro turbines
A hydraulic turbine is an engine that converts the energy of a water flow into rotational energy of a shaft.All used turbines are classified into active and reactive turbines.
The pressure at the inlet and outlet in active water turbines is the same, and its impeller uses only the kinetic energy of the supplied flow. For reactive turbines, the potential energy of the water flow at the inlet is greater than at the outlet. In addition, this type of turbine partially uses the kinetic energy of the flow.
In general, reactive turbines are classified into radial-axial, axial, and diagonal. Inside the radial-axial hydraulic turbines, the water flow will move radially before entering the impeller, and then in the axial direction.
In turn, the flow of water in the impeller of an axial hydraulic turbine maintains an axial direction throughout the entire length of the system. This group includes vertical and horizontal hydraulic turbines.
The choice of a water turbine for the construction of a hydroelectric power plant is carried out simultaneously with the choice of other hydromechanical equipment at the early stages of the engineering design of the facility. This choice is always based on the results of the most detailed technical and economic calculations, taking into account the operating conditions of the HPP.
When determining the most suitable unit, the engineering team proposes several options, for each of which the main operating parameters, investment costs, capacity and generation are calculated.
Equipment for water supply to hydraulic turbines
Turbine chambers are geometric structures that are installed to supply water to a turbine.Depending on the pressure of the water flow and other operating conditions, turbine chambers are made of metal or reinforced concrete.
The shape of the chamber is determined by the specific layout of the HPP equipment and the location of the hydraulic units in the turbine hall. The turbine chambers are calculated taking into account the main parameters of the hydraulic turbine, including the impeller diameter.
HPP engineering design pays attention to other hydraulic structures, such as pumping devices.
The latter are designed to drain water from the turbine into the outlet channel.
The pumping devices actually convert kinetic energy into pressure energy of the water stream.
Pumped storage power plants can be designed in different layouts. For example, a four-machine configuration of a pumped storage power plant assumes the installation of two independent pairs of machines. Firstly, it is a combination of a generator and a hydraulic turbine, and secondly, it is an electric motor paired with a water pump.
There is a two-machine configuration of a pumped storage power plant, in which a special hydraulic machine (turbine-pump) is used, as well as a combined electric machine (motor-generator), which perform different functions depending on the operation cycle.

Electrical equipment of the hydroelectric power plant
Hydro-generators are electrical units that convert the mechanical energy of rotation of the shaft of a hydraulic turbine into electricity.This equipment consists of a rotor and a stator.
Depending on the location, hydro generators are classified into horizontal and vertical.
When choosing equipment for large hydroelectric power plants, engineers, as a rule, give preference to vertical suspended or umbrella type hydro generators. Horizontal hydrogenerators, in turn, are used in many modern projects of small hydroelectric power plants with low-power turbines.
An important electrical equipment HPP is a transformer designed to change the voltage.
Since the transmission of electricity over long distances is carried out at high voltage, the substations of the hydroelectric power plant increase the voltage at the generator output in order to reduce costs.
The choice of transformers for hydroelectric power plants should be carried out after drawing up an electrical diagram. The layout of the facility is thought out so as to provide convenience and minimize the cost of installing electrical equipment.
The transformers are installed at specially equipped assembly sites.
High voltage switchgear can be open or closed. The latter are installed in special buildings that provide reliable protection of electrical equipment from extreme weather conditions (including built-in heating). Open switchgears are much cheaper in construction.
Hydromechanical equipment for HPPs
Hydromechanical equipment includes protective grids, gates, lifting mechanisms, transportation equipment, grating cleaning devices, etc.The choice of this equipment depends on the layout and operating conditions of the HPP.
Despite its apparent simplicity, properly designed hydromechanical equipment plays a key role in keeping the facility running smoothly.
For example, waste-retaining protective grids protect the turbine blades from the ingress of large particles that can disrupt the normal functioning of expensive hydraulic units and even stop the production of electricity.
Waterway gates can be used for a variety of purposes, including repairs and routine maintenance.
Lifting equipment such as cranes in machine rooms are widely used to replace multi-ton units.
Modern HPP requires numerous ancillary facilities and workshops to ensure equipment maintenance and continuous processes. In the engineering design of hydroelectric power plants, much attention is paid to security systems, elements of technical water supply, access roads, etc.
Are you interested in hydropower financing?
Are you looking for funding or a reliable general contractor for the construction of a hydroelectric power plant under an EPC contract?
GCAM will provide professional assistance to your business at any stage of the project.
Contact us to find out more.




















