After receiving the necessary documents and project presentation, our team will try to review your request as soon as possible, and leading experts will offer the best options for project funding.
Long-term loans, issuance and placement of bonds, public-private partnership mechanisms – all this contributes to the development of strategic projects in the face of a lack of financial resources and fierce competition for capital.
Further, the following aspects of financing investment projects will be considered:
• Development of long-term strategy for financing investment projects.
• Project budgeting and assessment of the cost of investment resources.
• Methods of financing and sources of funds.
GCAM Investment Group, an international company with roots, provides comprehensive services to large corporate clients in financing investment projects.
We offer long-term loans of 50 million euros and more, organize project finance (PF) schemes, and provide legal, organizational and financial support for large projects from A to Z.
Long-term investment strategy and project budgeting
The investment activity of a large company continues throughout the entire period of its life and must be carried out taking into account a certain time horizon.Planning and choosing directions for future investment activities is called the development of an investment strategy.
An investment strategy is a process of predicting long-term goals for the development of investment activity and choosing the most effective ways to achieve them based on forecasting the investment market conditions both in general and in specific sectors. The development of investment strategy is a complex process based on high-quality forecasting of the investment market, changes in the cost of capital and many other aspects of the investment environment.
In general, an investment strategy identifies opportunities to improve a company's performance through investment. It determines the direction of placement of funds in order to obtain the greatest income and achieve the greatest increase in assets with an acceptable level of risk.
Such a strategy is usually called active or aggressive when it comes to focusing on profit. Many companies prefer a passive strategy, in which the investor seeks to maintain or moderately increase key performance indicators while focusing on minimizing risk.
Project budgeting
The market approach to estimating project costs is used in the development of financial documentation.When drawing up a project estimate based on a comparison of market prices for machinery, equipment and materials, since most of them are widely traded on the international market and there is sufficient detailed information on the proposals of suppliers.
A detailed assessment of all positions is not always convenient, especially when it comes to comparing several complex proposals of large contractors / suppliers. When preparing construction estimates, a cheaper and faster method of aggregated indicators can also be used. It should be borne in mind that for some types of investment projects implemented in knowledge-intensive industries, the cost of purchasing a license, know-how and similar intangible assets should be added.
Also, when budgeting a project, the method of linking the budget to the cost of technological equipment is used. It is based on the accumulation and development of price information for projects in a number of industries, resulting in the determination of the approximate share of equipment in the total investment.
The budget as a project management tool performs the following functions:
• Planning of financial resources required to complete the entire cycle of work on the project.
• Monitoring compliance with the cost limits and prompt identification of deviations.
If the project estimate determines the overall need for business financing, then during the project implementation it becomes necessary to plan the expenditure of funds on an annual, quarterly and even monthly basis.
The project estimate distributed over time based on the work schedule represents the project budget. The project budget, like most other project documents, is subject to repeated adjustments during the implementation of the project as a result of clarifications of both the estimate and the work schedule.

Investment resources and their cost
Business investment activity is characterized mainly by the expanded reproduction of fixed assets, which requires the formation of the necessary investment resources.This process involves the separation of a significant part of the funds used for consumption and current projects.
Investment resources aimed at these purposes are diverted from the main business for the entire period until the commissioning of a new facility. In the future, these funds are gradually returned to the investor during the operation of facilities, the release and sale of manufactured products.
Investment resources can be classified by types of property:
• State investment resources: budget funds and extra-budgetary funds, state loans, as well as shares and other fixed and current assets belonging to the government and municipalities.
• Non-state investment resources, including resources of commercial and non-commercial entities, banks, public associations, and private investors. Such resources include internal and borrowed funds of companies, as well as funds of institutional investors, including joint investment institutions, non-state pension funds, and insurance companies.
In general, financial resources refer to income that is owned by enterprises, organizations and the state and directed to meet investment needs, expanded reproduction and growth of material well-being.
These financial resources cover the resources of all sectors of the economy, including the public and private sectors.
The main sources of financing for investment projects are loans.
A traditional bank loan can be provided by banks to expand production (investment loan) or as a source of payment for current activities (loan to replenish operating funds). Borrowed funds can also be provided by one enterprise to another in the form of a deferral of payment for goods sold or services provided.
Depending on the form of attracting investment capital, there are such methods of financing investment projects as budget financing, self-financing, share issue, loan financing, financing through grants and charitable contributions, project finance and mixed options.
Investment resources and cost of capital
The cost of investment capital is the required rate of return that a project must provide in order to cover the costs of raising capital in the market.The main factors that determine the cost of capital:
• Investment project risk.
• The share of debt in the capital structure.
• The current state and prospects for the development of the market.
• Financial stability of the business and other factors.
In the course of investment activities, companies use debt funds, attracting them in the form of investment loans from financial institutions, as well as in the form of bonds with a certain maturity and interest rate. The cost of capital received as a result of the issue of bonds is influenced by the same factors that determine the cost of an investment loan.
More precisely, the cost of capital raised from the issuance of bonds is calculated using the formula below:
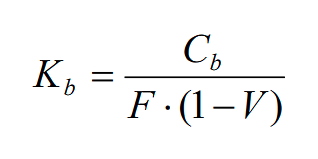
Kb – cost of capital from bonds;
Cb – annual coupon for issuing new bonds;
F – nominal value of bonds;
V – costs of issuing bonds to the nominal value.
Due to the fact that interest on loans and / or bonds is included in the cost of production of an investment project, the cost of debt capital must take into account the tax rate.
The formula for calculating the cost of bond capital will look like this:
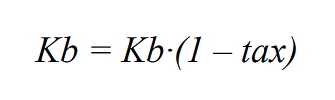
Kb – cost of capital from bonds;
tax – applied tax rate.
With regard to preferred shares, one of their important features is the payment of a fixed dividend or a declared percentage of the value of the share at the time of issue. The market plays a huge role in determining the dividend income from these stocks.
The determining factor is income from similar preferred shares, which are listed on the stock exchange.
The cost of capital from preferred shares is calculated using the following formula:
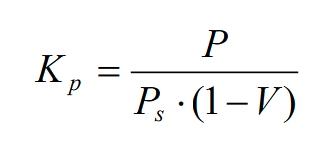
Kр – the cost of capital from the preferred shares;
Ps – market value of preferred shares;
V – the cost of issuing preferred shares;
Р – preferred dividend.
The cost of capital from common stocks is made up of three factors such as common stock price, dividends and dividend growth rate.
Thus, the formula for calculating the cost of capital obtained from ordinary shares will look like this:
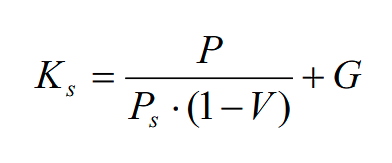
Ks – the cost of capital from the issue of ordinary shares;
Ps – the market value of ordinary shares;
V – the cost of issuing ordinary shares;
G – the constant growth rate of dividends;
P – dividends.
Self-financing of investment projects
The most attractive method of financing investment projects is self-financing, carried out exclusively at the expense of the internal funds of the enterprise.These include:
• Net income.
• Sums insured indemnification.
• Depreciation deductions.
• Surplus of fixed and working capital.
The main source of formation of investment resources for financing the project is profit, which is the difference between the total amount of income and the costs of production and sale of products.
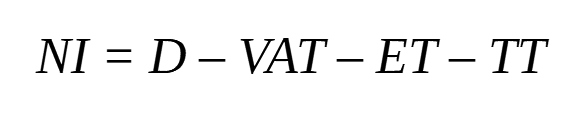
Income may arise from core operating activities, financial activities and investing activities. Thus, the real income of the project consists of the net income from the sale of products and services (NI), calculated by deducting from the income (revenue) from the sale of products (D), value added tax (VAT), excise tax (ET), other fees / taxes from turnover (TT) and other deductions from income.
The final financial result of the project (net profit or loss) is determined as the difference between all types of income and expenses for the reporting period.
The company can use profit as a source of financing investment projects only in small amounts and only in the part that goes to the formation of production development (for example, financing small investment measures or dangerous high-risk innovative projects).
An important source for self-financing of investment projects is depreciation deductions, which are formed as a result of the transfer of the cost of fixed assets to the cost of the product.
The method of financing investment activities described below is widely used to finance large investment projects with significant payback periods.
Investment loans for large projects
An important category is investment loan, which remains the main source of financing investment projects, and therefore an important lever in stimulating the development of the global economy.In essence, an investment loan is an economic relationship between a lender and a borrower regarding the financing of investment activities on the basis of repayment in a certain period with interest payment. This relationship is characterized by the movement of value (borrowed capital) from the lender to the borrower and in the opposite direction.
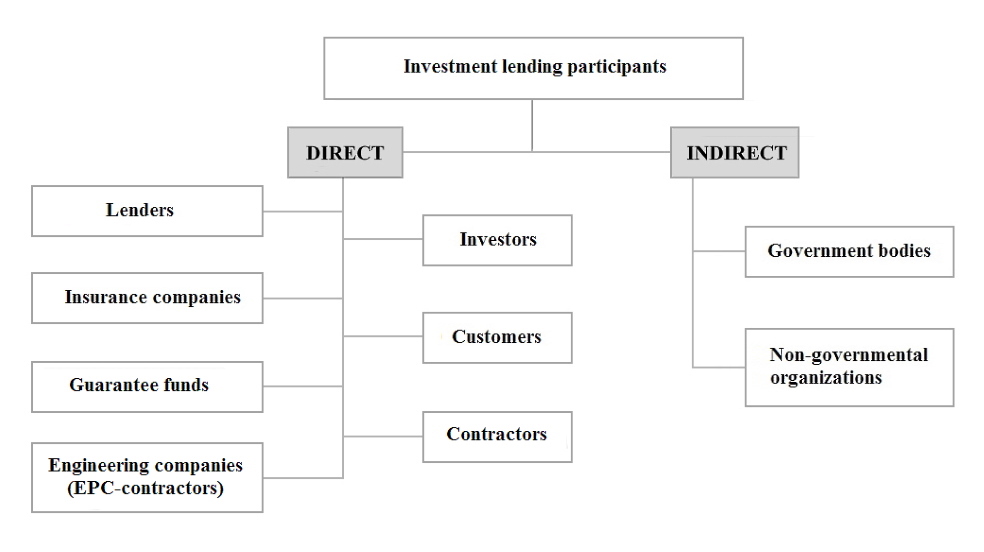
All subjects of investment lending are divided into direct and indirect.
Direct entities, as it follows from the definition, directly participate in the process of investment lending, and timely payment of the loan to the creditor depends on them.
Indirect entities participate in lending indirectly, creating favorable conditions for attracting, using and repaying loans issued to finance investment activities.
Bank investment loan is the main form of investment loan, in which money for financing projects is provided by banking institutions.
The main types of bank investment lending include the so-called revolving loans, long-term project loans and underwriting.
Investment loans to large businesses are intended for financing long- and medium-term investments, such as the purchase of equipment or the construction of buildings, usually with a term of more than one year. In most cases, the initiator of the project applies for a large loan based on a detailed business plan and an approved estimate. The cost of loan capital in such cases directly depends on such factors as the type of project, financing period, reputation of participants, etc.
A revolving credit line allows the borrowing company to periodically borrow funds within the specified limit, repay the full amount or its part and, if necessary, carry out repeated borrowing within the term of the loan agreement.
A relatively new form of investment lending is the financing of long-term projects by buying out issues of industrial bonds issued by clients. In international practice, this is called underwriting. Underwriting refers to the conclusion by a securities trader of contracts for the alienation of securities or the provision of services related to such alienation in the process of issuing these securities on behalf of and at the expense of the issuer on the basis of a contract with the issuer.
The amount of an investment loan depends on the financial health of the borrower, the type and cost of collateral, and the total cost of the project. Commercial banks usually finance no more than 70-80% of the project cost.
The loan can be secured by various assets of the project sponsor or SPV:
• Rights to receive cash flows generated as a result of the investment project.
• Property rights to funds placed on deposit accounts in banks.
• Assets created as a result of an investment project.
• Special purpose vehicle (SPV) corporate rights etc.
An important factor determining the attractiveness of an investment loan is the possibility of early repayment of the loan at any stage.
It is also worth paying attention to important technical nuances, such as collateral insurance. In particular, collateral insurance in the practice of investment lending is mandatory and is usually carried out in insurance companies accredited by a particular bank.
Financing investments by issuing bonds
The issuance of stocks is one of the most common ways to finance investment projects.The authorized capital of a joint-stock company is formed from the value of shareholders' contributions made as a result of their acquisition of stocks, so the issue of additional shares allows companies to attract significant resources for the implementation of investment plans.
A joint stock company may be created by legal entities who bear joint and several liability for the obligations that have arisen. The main financial instrument in attracting investment resources with this method of financing is a stock. An example of stock classification is shown in the table below.
Table: Classification of stocks.
| Type of stocks | Brief description |
| Blue-chip stocks | These securities are issued by the largest and most reputable companies (for example, General Electric), which are leaders in their industries, and most importantly, have consistently paid dividends to shareholders throughout their history. Investing in the purchase of these stocks is not considered risky, so they are popular among most investors, and their prices remain high even in the face of market uncertainty. |
| Income stocks | These are stocks of telephone companies, water, gas, electricity supply companies, as well as other utility companies, the dividends of which exceed the average level. This is explained by the fact that such corporations work stably and have well-predicted sources of income. Investors buy these stocks because they are sure that their value will only increase over time. |
| Growth stocks | These are shares of corporations whose revenues and profits are above the average level, but the payment of dividends usually does not exceed 35%. Such a dividend is explained by the company's desire to primarily finance scientific research and development, as well as expanding the scale of production and sales. Therefore, despite the low current dividends, many investors prefer these securities, hoping that they will bring large profits in the future and their market value will increase significantly. |
| Cyclical shares | The price of these securities rises and falls in sync with the ups and downs in the economy. Basically, these are stocks of corporations in the basic branches of the economy, such as metallurgy, automobile manufacturing, raw materials industries, semiconductor industry, etc. Investors try to buy such stocks when it comes to expanding production and sell them before the recession begins. |
| Counter-cyclical stocks | These are stocks of companies whose price is relatively stable even with a downturn in the economy as a whole. Such corporations do not change their dividend policy depending on cycles in economic development and therefore pay their shareholders almost constant dividends. Many securities of this type are simultaneously classified as income stocks. |
| Penny stocks | This is the name of stocks of young companies. These securities are often sold "over the counter" or on specialized speculative exchanges. They cost much less than the stocks of well-known corporations, however, by buying them, investors accept a great risk. |
Practical aspects
The issue of stocks, as well as founders' contributions to the authorized capital of the company, open numerous opportunities for partial financing of investment projects.
Equity financing of investment projects can be carried out in the following main forms:
1. Conducting an additional issue of stocks by the existing joint-stock company for the purpose of financial support for the implementation of the investment project.
2. Attracting additional funds (investment contributions, shares) of the founders of the existing enterprise to ensure the smooth implementation of the project.
3. Creation of a new company (special purpose vehicle, SPV) designed specifically for the implementation of an investment project.
The additional issue of stocks is used to implement large-scale projects, development investment programs, sectoral and / or regional diversification of investment activities.
The use of this method mainly for the financing of large investment projects is explained by the fact that the huge costs associated with the issue can be justified only by significant amounts of resources attracted.
The main advantages of issuing stocks as a method of financing projects:
• Payments for the use of attracted resources are made depending on the financial result of the joint-stock company (SPV).
• The actual use of investment resources has a significant scale and is not limited by terms, as in the case of a loan agreement.
• The issue of stocks allows project initiators to attract necessary financial resources at the beginning of the project, as well as to postpone the payment of dividends until the period when the investment project begins to generate income.
• Shareholders can control the targeted use of funds for the needs of a specific project.
However, this method of financing investment projects has a number of significant limitations.
Thus, a joint-stock company receives investment resources upon completion of the placement of the issue of stocks, and this requires time, additional costs, evidence of financial stability, information transparency, etc.
The procedure for the additional issue of stocks is associated with registration, listing, and significant operating costs.
During the issuance procedure, issuing companies bear the costs of paying for the services of professional securities market participants who perform the functions of an underwriter and investment consultant, as well as for the registration of the issue. It should also be taken into account that the issue of shares cannot always be placed in full. In addition, after the issue of stocks, the company must pay dividends, periodically send reports to its shareholders, etc.
Additional emission of stocks leads to an increase in the share capital of the company.
The decision on an additional issue may lead to the dilution of the former shareholders' shares in the authorized capital and reduce their income, although the legislation of most countries gives the first shareholders a preemptive right to purchase newly placed stocks.
A joint-stock company that is going to finance an investment project through an additional issue of stocks must develop an effective strategy for increasing the liquidity and value of its securities. This strategy, in particular, provides for increasing financial transparency and openness of information about the issuer, expanding and developing core business activities, increasing capitalization, improving financial health and improving the image.
Macroeconomic aspects
Attracting investment resources to finance an investment project through the issue of stocks makes it possible to mobilize funds to improve the quality of the production base and solve the problems of financial support for the reproduction of fixed assets.In the macroeconomic context, this method of financing investment projects can play a role in the transformation of state economic policy.
The distribution of stocks among companies leads to a rational redistribution of solvent demand.
The purchase of stocks by private investors contributes to the transformation of consumer demand into investment demand, mediates the outflow of capital from the consumption to the accumulation fund, thereby shifting the pressure of money not backed by goods from the market of consumer goods to the market of production tools. The equity form of financing investment projects greatly facilitates the process of integration of the national economy into the system of global economic relations, attracting investments from foreign companies.
Issuance and placement of securities by large national companies on world markets should contribute to attracting additional resources for development, modernization and reconstruction of the industrial base. The use of the financial market makes it possible to manage larger impersonal productive investments of small shareholders compared to the creation of joint ventures.
Government support of investment projects
Government (public) financing of investment projects includes public investments in major projects important for economic and social development.Public financing is characterized by specific forms of providing budget allocations.
Financing of capital investments from the state budget in a market environment has a number of features. The state actively intervenes in the financial support of state-owned enterprises. Along with public funds, private funds, foreign investments, and loans from international financial institutions are also involved in such projects.

Table: Principles of public financing of investment projects.
| Principles | Brief description |
| Achieving the maximum effect from public funds | Among the desired effects of an investment project with government support can be the solution of various tasks of the social and economic development of the state or region, the growth of government or municipal income, and so on. The practical implementation of this principle is based on the rational management of budget funds (allocation of funds for a specific program), the tender approach and the use of advanced project management tools. |
| Targeted use of budget resources | This principle means that the allocation of public funds is carried out in accordance with the purpose of the approved budget. This principle also contributes to increasing the efficiency of budget expenditures. |
| The principle of combining private and public funding sources | When determining the scale of financing an investment project, the availability of internal resources, opportunities for obtaining a bank loan and other funds is taken into account. Attracting public funds is usually carried out as a last resort considering the complexity of this type of financing. |
| Funding according to the actual progress of the project | Allocation of public funds taking into account the achievement of KPIs and the actual use of previously provided resources. Linking budget financing with specific results of the activities of enterprises and organizations allows for better financial control in those areas of activity that are financed from the central or municipal budget. |
| Non-refundable financing | The principle of non-refundable financing is usually applied to strategically important public-private projects (for example, energy projects, infrastructure projects, health care projects and so on). |
Some requirements for investment projects financed with public funds:
• Compliance of the project with the criteria and defined priorities determined by the relevant government bodies or local authorities.
• Clear goals of the project, which may include a certain level of profit, payback period, creation of new jobs, increase in tax revenues to the regional budget, etc.
• A real opportunity to achieve maximum efficiency in the use of government funds.
The experience of European countries shows that the state plays a decisive role in financing specific state-wide structural investment programs.
The issue of evaluation and control of such investments at all levels becomes extremely important.
Authorities impose certain requirements on banks that finance public-private investment projects, as well as on the projects initiators. In particular, an important role in the choice of private partners is played by tax discipline, a long and successful operating history, financial health, and so on.
If you are interested in long-term financing for your investment project, contact GCAM Investment Group for advice.
We offer financing for capital-intensive projects in energy sector (including renewables), mining and processing of minerals, oil and gas production (including LNG investments), heavy industry, agriculture, real estate, tourism and other industries.
In particular, our team can provide you with credit guarantees and act as a mediator in negotiations regarding the implementation of ambitious public-private projects in EU countries and outside Europe.




























