Financing and construction of sugar factories
GCAM Investment Group offers:
• Investment financing from €50 million and more
• Minimizing the contribution of the project promoter
• Investment loan term up to 20 years
• Loan guarantees
Brazil and India remain the world's largest sugar producers and continue to compete with each other.
It is expected that global sugar consumption will continue to grow in the coming years, which requires an increase in production and the use of more efficient approaches in financing the construction and modernization of sugar refineries.
GCAM Investment Group is ready to offer long-term financing for the construction of sugar refineries around the world, including loans with a maturity of up to 20 years.
We successfully work with large companies from Spain, USA, Great Britain, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Mexico, Brazil, etc.
Our range of services includes, but is not limited to:
• Investment financing.
• Investment engineering and consulting.
• Long-term business lending.
• Project finance schemes (PF).
• Financial modeling.
• Credit guarantees.
Are you looking for a major source of project financing in the agricultural sector or the food industry?
Do you need a reliable partner with broad financial and technical capabilities?
Contact an GCAM representative for more information.
Mechanisms for financing sugar refineries
The sugar industry is often viewed as a guarantor of the state's food security.The financing of sugar refinery projects and ensuring their continuous operation directly affects related industries that are inextricably linked with sugar refineries.
Given the need for further development of the sugar industry, company management and government officials should carefully analyze the availability and efficiency of the use of financial resources, as well as the sources of their formation.
Financial resources are often referred to as the "blood" of a business, as it is the only highly mobile resource that can be easily transformed directly into any other type of material resource. Finding, attracting and using financial resources for the construction, modernization and expansion of sugar refineries are the most important tasks for project teams.
In modern realities, the sustainable development of the sugar industry largely depends on the ability of companies to attract significant financial resources for the implementation of large-scale projects, including the construction, modernization and expansion of sugar factories. Among the most effective ways to attract resources for the development of activities are long-term investment lending, bonded loans and leasing instruments.
Project finance (PF) schemes, implemented through specially created independent companies, over the past decades has become one of the most effective ways to finance large industrial and agricultural projects with limited recourse.
The choice of the most suitable sources of financing for the investment needs of sugar refineries is carried out taking into account the specifics of the project. The volume and structure of funding sources are influenced by the type of enterprise, ownership, structure, business goals for a certain period of time, the internal financial policy of the company, external factors, etc.
The ability of companies to attract financial resources from various sources for the construction or expansion of sugar refinery projects opens up significant development opportunities.
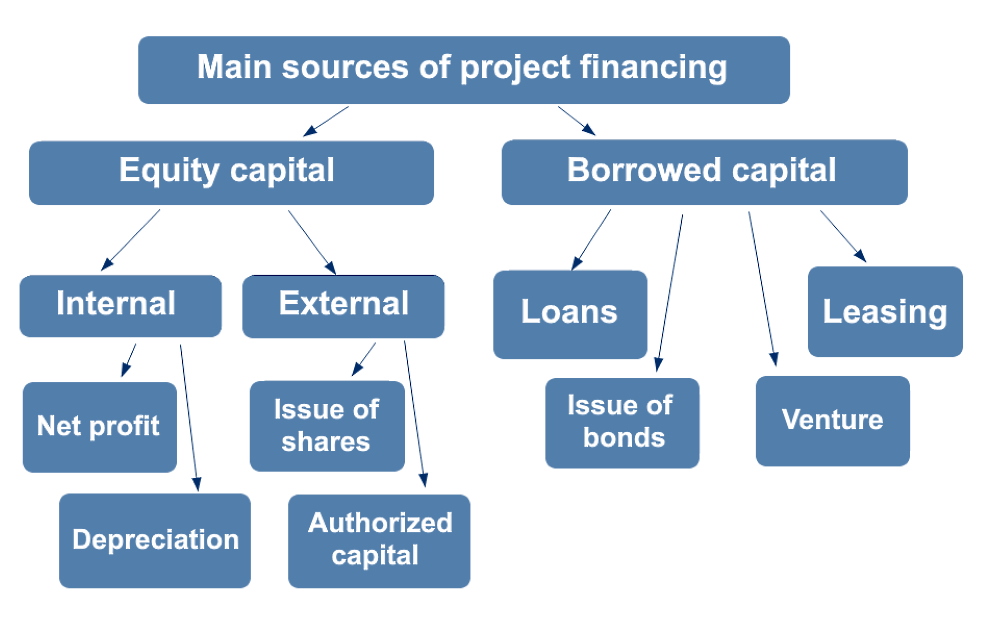
Traditionally, all sources of financing investment costs are divided into equity and borrowed capital. In turn, equity capital is divided into two groups:
• Internal resources: depreciation, proceeds from the sale of non-current assets, compensation for losses under insurance contracts, current assets invested in the project.
• External resources attracted through additional contributions to the authorized capital of the company, the issue of shares, grants, as well as the use of tax incentives.
Borrowed sources of financing for sugar refineries include funds received from bank loans, a tax investment loan, tax incentives, leasing, factoring, sales, forfaiting agreements, corporate bonds, charitable contributions, under the terms of crowdfunding, fundraising, etc.
Of course, the latest sources difficult to apply in the context of the sugar industry.
Important sources of financing for new projects are net income and depreciation charges that companies accumulate. However, the use of equity capital for investment purposes is currently limited, and these funds are usually used for day-to-day operations.
The use of equity capital to finance the investment needs of companies is constrained by such factors as significant debt, high tax rates, market uncertainty, etc. With the increase in the level of profitability of sugar refineries, the easing of tax pressure and the reduction of unproductive costs, their role as investment sources will grow.
A special role in the financing of the sugar industry is played by loans provided by state, commercial banks and even international financial institutions (IFIs). Their share in the industry's financing structure remains quite high, but banks impose strict requirements on potential borrowers. Moreover, growing economic and geopolitical unpredictability reduces the appetite of banks for long-term projects, forcing them to limit financing to short-term lending.
Bank lending and other loans remain attractive investment opportunities for many sugar producers due to the quick and easy fundraising process.
Not the last place in the decision of owners belongs to the lack of potential influence of creditors on the ownership structure of the borrowing company (as opposed to the issue of new shares).
Mention should be made of such sources of attracting investment resources as leasing (providing to the lessee for use for a certain period of equipment that is the property of the lessor or acquired by him on behalf and in agreement with the lessee). Leasing tools are especially useful in the context of purchasing expensive equipment for sugar refineries, such as vacuum machines, pumps, disc filters, beet washers, beet elevators, etc.
Another important source of funding for sugar refinery projects is government financial support, which can be allocated to modernize or build new facilities. These funds can be provided by the central government or local governments in the form of directed lending, as well as grants, grants and subsidies to sugar producers to support the sector.

An insignificant role in the structure of sources of financing for sugar refinery projects is played by tax incentives, which allow numerous companies in the sector to use additional funds to expand and modernize production.
The experience of developing countries in providing tax incentives is controversial.
While some countries have made significant progress in financing industry and agriculture, other countries have noted the negative consequences in the form of abuse of benefits and stopped such support.
Foreign investment as a source of financing can contribute to the development of the sugar industry in countries with high investment attractiveness. Attraction of foreign capital prevents possible monopolization of the market, and creates favorable conditions for the introduction of innovative solutions. However, it should be remembered that foreign capital is extremely limited in regions of the world that are characterized by geopolitical instability, weak economic development and imperfect financial markets.
Project finance in the construction of sugar refineries
Project finance (PF) schemes are widely used in world practice to finance projects in capital-intensive industries such as heavy industry, mining and processing of minerals, oil and gas sector, etc.However, the advantages of this financing model have recently extended to other sectors, including the sugar industry and the agricultural sector in general.
Project finance allows companies to raise significant financial resources without collateral, using the project's future cash flows to repay debt. This is a highly complex model based on a multilateral contractual structure and multiple guarantee and security instruments.
Some features of project finance in the construction of sugar refineries:
• High capitalization of the project, which allows to completely solve the problems of construction, launch, operation, production and marketing of products.
• Participation in the construction of reputable partners prepared for long-term cooperation.
• Professional feasibility study of the project and its preliminary approval with banks that are ready to provide financial resources for the project or act as a guarantor.
• A clear definition of project risks and their rational distribution among project participants for the most efficient project implementation.
Like most other financial terms, the term "project finance" is interpreted differently in world practice.
For example, in Europe it is used to describe a whole range of tools and methods for attracting the necessary financial resources. In the United States, the term "project finance" refers to a special type of financing in which the income received from the implementation of the project is the main or only source of debt repayment.
The traditional approach to financing large projects involves the active participation of the initiators, who bear the bulk of the investment costs.
But companies that are not ready for significant capital investments prefer to use project finance with its high financial leverage.
Modern financing schemes make it possible to shift up to 80-90% of investment costs onto the shoulders of creditors and investors, limiting themselves to the minimum participation of initiators.
This is especially attractive for companies that do not have enough free resources and are not able to provide high-value assets as collateral.
Project finance methods were originally used in banking practice to describe certain financial and commercial schemes that make it possible to reduce the risks of non-payment of debts, as well as the risks associated with the purchase and operation of equipment. PF allows companies to establish long-term relationships with suppliers of equipment and materials, as well as to enjoy the support of reputable financial institutions, including budgetary support.
A professional calculation of cash flows allows, at the initial stage of designing and launching a sugar refinery, to assess the real financial capabilities of its owners and the need for borrowed or attracted funds, determine the expected profit after the enterprise is put into operation, and distribute the risks of construction and operation among all participants (shareholders) of the project.
In a broad sense, project finance is financing based on the viability of the project, without regard to the creditworthiness of its participants, their guarantees or guarantees for loan repayment provided by third parties.
Sources of debt repayment under PF are mainly cash flows of the project generated after its launch.
Currently, setting up a PF may involve the use of complex financing mechanisms such as securitization and mezzanine financing. In addition to instruments such as bond issuance and lending, leasing agreements are promising levers of project finance.
All investment financial resources of a company planning to implement an investment project of a sugar refinery or other facility can be divided into two main groups, equity and borrowed capital (as shown in the figure below).
The use of each of the sources of project financing has both positive and negative consequences for the project and its participants.
The advantages of internal sources of financing for the construction of a sugar refinery include:
• High capital mobility.
• High efficiency in terms of return on investment.
• Reducing the risk of bankruptcy of the company.
• Maintaining control over the company by the owner.
Disadvantages of internal funding sources include the following:
• Limited resources that are also needed to finance current activities.
• Lack of external control over the efficient use of investment resources, which often leads to severe financial consequences in case of unskilled management.
• Failure to use the opportunities to increase the return on equity by attracting borrowed funds (failure to use the effect of financial leverage).
A company that uses internal resources to finance a project can count on higher stability, but pays for this with a limited pace of project implementation. Given the dynamic changes in the market for sugar and related products, the loss of time can be costly for the initiators.
Borrowed capital and external sources are characterized by the following advantages:
• Wide range of funding sources.
• Independent control over the effectiveness of the use of funds and the project as a whole.
• Wide opportunities to attract huge financial resources to the effect of financial leverage.
• Retaining opportunities to use internal resources for other purposes.
The disadvantages of these sources include the following factors:
• The complexity of raising funds and the numerous requirements of creditors.
• A lengthy financing procedure that could disrupt the company's plans.
• The need to provide guarantees or adequate credit collateral, which can be provided by the company's highly liquid assets.
• The need to pay part of the profits to pay interest, coupons and dividends, which reduces the share of funds allocated to finance the needs of expanding sugar production.
• The probability of bankruptcy in case of untimely repayment of debt.
• Loss of control over the business when issuing shares, etc.
Despite numerous risks and limitations, borrowed funds are widely used for project finance. In typical sugar mill projects, these funds account for at least 50% of the total investment cost.
Long-term investment loans for sugar refineries
This is a type of long-term financing that companies receive through banks for the implementation of capital-intensive investment projects, such as the construction / modernization of sugar factories, warehouses and other facilities.An investment loan is one of the most frequently used ways for companies to obtain financing today.
Almost all such loans are issued by commercial banks that manage the company's current accounts and also provide other financial services to the company. Often these are financial institutions or banking syndicates that have a high lending capacity in accordance with applicable banking laws and regulations.

As sugar producers turn to commercial banks for financial resources, the choice of a bank deserves careful consideration.
The company must be confident that the lender will be able to help the company meet the needs for investment funds and serve its interests in a certain time horizon.
Table: Advantages and disadvantages of investment lending for sugar refineries.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Wide opportunities for negotiations and agreement on mutually beneficial terms of project lending. | Strict conditions for granting loans, including possible restrictions on the current activities of the company. |
| The ability to quickly obtain large borrowed funds that are unrealistic to attract from other sources. | Most banks require strong guarantees or backing loans with highly liquid assets. |
| A loan, unlike the issue of shares, does not affect the ownership structure of the company if the financing is properly organized. | The company must carefully plan its projects because it will have to pay periodic payments for a long time. |
Signing a loan agreement to finance the construction or modernization of a sugar refinery requires certain skills and competencies from the borrowing company.
Company representatives must provide the following:
• Feasibility study of the project.
• Business plan including funding requirements.
• Detailed financial plan with payment schedule.
• Confirmation of solvency and liquidity.
It is important to provide the bank with a clear business project development plan that allows you to repay the loan within a certain period of time.
For larger loans, a range of guarantees is required.
The cost of building sugar refineries can reach several tens of millions of euros, so preparing for the lending process requires some efforts from all parties. The professional assistance of an experienced financial team can bring your business closer to obtaining financing on favorable terms.
If you are looking for a loan to build a sugar factory or upgrade equipment, contact the GCAM Investment Group financial advisor in your area.
We are ready to provide you with professional services in the field of project finance, financial modeling, investment engineering and consulting.




















